The past decade has witnessed remarkable advancements in positioning and navigation systems, particularly in RTK GPS technology. From its early applications in surveying to its integration in autonomous vehicles and precision agriculture, rtk gps has transformed industries by providing centimeter-level accuracy in real time. This article explores the evolution of RTK GPS technology over the last ten years, highlighting key developments, applications, and future trends.
Understanding RTK GPS Technology
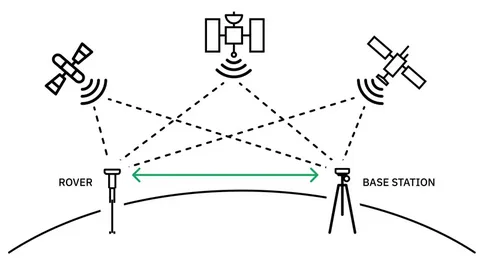
RTK, or Real-Time Kinematic GPS, is a satellite navigation technique that enhances the precision of standard GPS. While traditional GPS provides accuracy within a few meters, RTK GPS reduces this margin to mere centimeters by correcting signal errors in real time. The system relies on a base station that transmits correction data to a rover or mobile receiver, enabling highly precise positioning.
Key Developments in RTK GPS Technology Over the Last Decade
1. Improved Satellite Constellations and Signals
Over the past ten years, the number of satellites and the quality of signals available for RTK GPS have increased significantly. The integration of multi-constellation systems such as GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou has enhanced positioning reliability and accuracy, even in challenging environments like urban canyons and dense forests.
2. Advancements in RTK Network Infrastructure
RTK GPS technology has benefited greatly from the expansion of networked correction services. VRS (Virtual Reference Station) networks and cloud-based correction systems have made it easier for users to access high-accuracy positioning without maintaining their own base stations. This has democratized the use of RTK GPS across multiple industries.
3. Miniaturization and Integration
Modern RTK receivers are smaller, more energy-efficient, and easier to integrate into drones, autonomous vehicles, and handheld devices. This miniaturization has enabled real-time, high-precision navigation in applications that were previously impractical or too costly.
Applications Driving RTK GPS Adoption
The evolution of RTK GPS technology over the last decade has unlocked numerous applications:
- Precision Agriculture: Farmers use RTK GPS for accurate planting, fertilization, and harvesting, increasing crop yields and reducing waste.
- Construction and Surveying: High-accuracy mapping and machine control systems rely on RTK GPS for efficient and precise operations.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars and drones utilize RTK GPS for accurate navigation and obstacle avoidance.
Future Trends in RTK GPS Technology
As RTK GPS technology continues to evolve, several trends are shaping its future:
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning: Predictive correction and smart signal processing will further improve accuracy and reliability.
- Global RTK Coverage: Expanding satellite constellations and network services aim to provide seamless global RTK GPS access.
- Cost Reduction: Advances in hardware and software will make high-precision positioning more affordable and accessible for small businesses and individual users.
Conclusion
The evolution of RTK GPS technology over the last decade has been marked by significant improvements in accuracy, reliability, and accessibility. From multi-constellation support to network-based corrections and miniaturized receivers, RTK GPS has become a cornerstone of modern navigation and precision applications. As the technology continues to advance, its impact across industries is expected to grow even further, shaping the future of autonomous systems, agriculture, surveying, and beyond.